Services
Complete Physical Examinations, pre Employment physicals, School Sports physicals
The general medical examination is a common form of preventive medicine involving visits to a general practitioner by well feeling adults on a regular basis. This is generally yearly or less frequently. Very important to create a personalized preventive plan and find hidden problems.

Preventive Medicine
Consists of measures taken for disease prevention, as opposed to disease treatment. It is recommended that adults and children aim to visit their doctor for regular check-ups, even if they feel healthy, to perform disease screening, identify risk factors for disease, discuss tips for a healthy and balanced lifestyle, stay up to date with immunizations and boosters, and maintain a good relationship with a healthcare provider.

Diabetes Mellitus
High blood sugar levels over a prolonged period due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Prevention and treatment involve maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical exercise, a normal body weight, and avoiding use of tobacco. Control of blood pressure and maintaining proper foot care are important for people with the disease. Treated with medications with or without insulin.

Asthma
Is a common long term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. Caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Is recommended to have early treatment to prevent complications.

Blood Pressure control
Blood pressure varies depending on situation, activity, and disease states. May be of sudden onset or of long duration. Long term hypertension is a risk factor for many diseases, including heart disease, stroke and kidney failure.

Heart Disease
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally. It is estimated that 90% of Cardio Vascular Disease is preventable by decreasing risk factors through: healthy eating, exercise, avoidance of tobacco smoke and limiting alcohol intake and treatment of diabetes and high blood pressure.

Gastrointestinal Diseases
Refers to a problems from mouth to rectum including liver, pancreas, gallbladder. Diseases on these organs are very common and at times difficult to diagnose. Many therapies available.
Respiratory Diseases
Range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, to life-threatening entities like bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, acute asthma and lung cancer. Various forms of treatment that help dilate major air passages and improve shortness of breath can help control symptoms and increase the quality of life for people with the disease.
Neurological diseases
Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness, headaches. Interventions for neurological disorders include preventative measures, lifestyle changes, physiotherapy or other therapy, neurorehabilitation, pain management, medication, or operations performed by neurosurgeons.
PROCEDURES / TESTS

Electrocardiograms
To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart’s muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.

Spirometry
Is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs), measuring lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is an important tool used for generating pneumotachographs, which are helpful in assessing conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD.

24 Hours Holter Monitor
Is a portable device for continuously monitoring various electrical activity of the cardiovascular system for at least 24 hours. The Holter’s most common use is for monitoring heart activity (electrocardiography or ECG). Its extended recording period is sometimes useful for observing occasional cardiac arrhythmias which would be difficult to identify in a shorter period of time.

Use of Nebulization
Is a drug delivery system used to administer medication in the form of a mist inhaled into the lungs commonly used for the treatment of cystic fibrosis, asthma, COPD and other respiratory diseases or disorders.
Biopsy
Medical test commonly performed by a physician involving extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease.

Removal of small lesions
Procedure done usually under local anesthesia to remove pathological lesions from the skin with scalpel, liquid nitrogen or electrocautery.
Urine Test
A urine test strip or dipstick test is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient’s urine in standard.
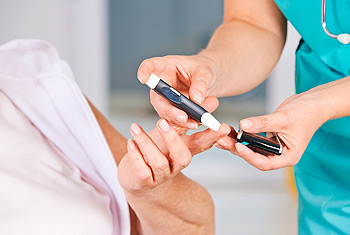
Blood sugar test
Test taken from a non-fasting subject. The reference values for a “normal” random glucose test in an average adult are 79 – 140 mg/dl (4.4 – 7.8 mmol/l), between 140 – 200 mg/dl is considered pre-diabetes, and > 200 mg/dl is considered diabetes according to ADA guidelines.
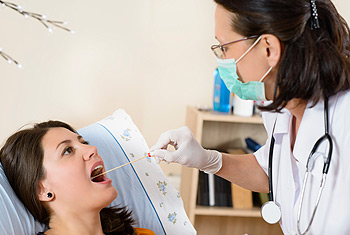
Strep Test
Is a rapid antigen detection test (RADT) that is widely used in clinics to assist in the diagnosis of bacterial pharyngitis caused by group A streptococci (GAS), sometimes termed strep throat.
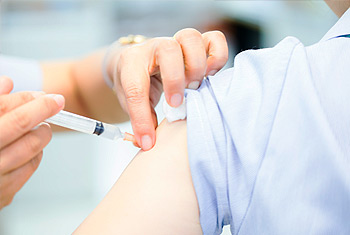
Vaccinations
Is the administration of antigenic material (a vaccine) to stimulate an individual’s immune system to develop adaptive immunity to a pathogen. Vaccines can prevent or ameliorate morbidity from infection. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified; for example, the influenza vaccine.
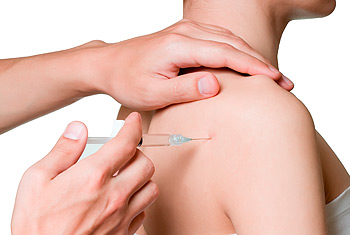
Joint injection
Procedure used in the treatment of inflammatory joint conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, tendinitis, bursitis, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome,[1] and occasionally osteoarthritis. A hypodermic needle is injected into the affected joint where it delivers a dose of any one of many anti-inflammatory agents, the most common of which are corticosteroids.
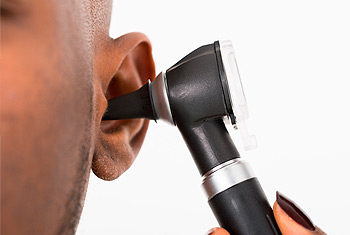
Ear lavage
Excessive earwax may impede the passage of sound in the ear canal, causing conductive hearing loss. The most common method of cerumen removal is syringing with warm water. Once the cerumen has been softened, it may be removed from the ear canal by irrigation.


